 |
 |
- Search
| Neonatal Med > Volume 29(2); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Cranial ultrasound (CUS) is an initial screening imaging tool used to evaluate the neonatal brain. It is an accessible, inexpensive, and harmless technique that can be used at bedside as frequently as required. Timely focused CUS in the neonatal care unit can play a major role in the diagnosis, follow-up, and management of brain damage. Despite the increasing use of point-of-care ultrasonography by intensive care physicians, neonatologist-performed CUS remains unusual. This review aims to provide an overview of neonatal CUS to neonatologists, focusing on the optimal settings, standard planes of the brain, and main pathologies in preterm infants. Adding Doppler studies allows evaluation of the patency of intracranial arteries and veins, flow velocities, and indices. This may provide an opportunity for earlier targeted circulatory support to prevent brain injury and improve long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes.
뇌 초음파(cranial ultrasound)는 신생아의 뇌를 검사하는 기본적인 영상 검사기법이다. 아직 닫히지 않은 천문들을 통해 뇌의 손상과 구조적인 이상을 확인하고, 손상의 시기와 변화를 신속하게 감지하여 진단과 치료에 이용하며 나아가 뇌의 성장과 성숙을 추적하기에 용이하다. 이동식 초음파 검사는 검사실로의 이동, 방사선 노출, 진정 등이 필요 없어 안전하고 반복적으로 실시할 수 있다[1,2]. 신생아에서의 뇌 초음파는 기기의 발달, 다양한 음향창(acoustic window)의 활용 등으로 인해 검사의 정확성이 향상되고 있으며3), 도플러 초음파는 순환 관리 및 치료 결정에 도움이 되는 혈역학적 정보를 제공한다[4].
임상의가 직접 환자의 침상에서 검사하고 이를 진단 및 처치에 적용하는 현장 초음파(point-of-care ultrasound)의 신생아집중치료실(neonatal intensive care unit, NICU)에서의 활용은 전 세계적으로 증가하는 추세이나, 나라마다 병원마다 차이가 크다[5,6]. 아직 국내에서는 신생아 의사에 의한 뇌 초음파 시행이 활발하지는 않은 실정이다. 그러나 대부분의 병원에서 숙련된 영상의학과 전문의에 의한 초음파 검사는 항시 이루어지기 어려운 반면, 신생아 의사들은 항상 NICU에 상주하고 있고, 빠르게 변하는 환자의 상태와 치료에 대해 가장 잘 알고 있다는 점을 고려한다면 신생아 의사가 환자에게 가장 적합한 시기에 NICU 현장에서 뇌 초음파를 시행하는 것은 충분히 가능하며 필요하겠다[5,7].
저자들은 NICU에서 뇌 초음파를 직접 시행하려는 신생아 의사들이 초음파 기기를 적절하게 설정하고, 보다 좋은 영상을 획득하고 해석하는 데에 도움이 되고자 신생아 뇌 초음파에 대해 알아보고자 한다.
뇌 초음파 시행에 정해진 금기 사항은 없으며, 뇌손상의 위험이나 가능성을 가지는 모든 신생아에게 적용할 수 있다[3]. 머리둘레의 비 정상적인 증가, 뇌출혈이나 뇌실질 이상, 뇌실확장, 혈관이상, 저산소허혈뇌손상, 치료적 저체온요법이나 체외막산소 등의 기계 적용 시, 선천성 기형, 중추신경계 장애의 증후나 증상, 뇌 감염, 머리 외상, 두개골조기유합, 산전 검사에서의 이상 소견 등 다양한 출생 전, 후기 상황에서 뇌 초음파 검사가 필요하다[8]. 특히 미숙아에서는 뇌 출혈 여부를 파악하기 위해 선별검사가 필요하며, 만삭아에서도 주 산기 저산소허혈뇌병증(hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy) 등의 특정한 상황에서는 병변의 변화와 뇌혈류 등을 파악하기 위해서 반복 검사가 필요할 수 있다[3].
미숙아의 선별검사 시기는 나라별로 다양하다[9]. 최근 발표된 미국 소아과학회의 가이드라인에서는 신경계 증상이나 징후가 없더라도 재태주령 30주 미만의 모든 미숙아와 30주 이상의 미숙아 중 위험인자(태반 박리, 소생술의 필요성, 저혈압, 심한 산증, 지속되는 기계환기, 패혈증, 기흉 등)를 가진 경우에는 선별검사를 시행하도록 제안하고 있다. 첫 검사는 출생 7일 이내에 시행하고, 생후 4–6주 및 교정 만삭시기(또는 퇴원 시)에 재검사하도록 제안한다[10]. 특히 28주 미만 또는 1,000 g 미만의 미숙아에서는 좀 더 집중적인 검사가 권장되는데, 출생 1일(선택적), 3일, 7일, 14일, 21일 (불안정 상태 시), 28일, 그 이후에는 교정 34주까지 2주마다, 그리고 교정 만삭시기에 검사하도록 권고하였고, 출혈 후 뇌실확장 (posthemorrhagic ventricular dilatation, PHVD)이나 임상적인 악화가 있으면 더 자주 검사하도록 권고하고 있다[11]. 캐나다 소아과학회는 32주 미만의 미숙아에게 생후 4–7일째 첫 검사, 4–6주에 재검사를 시행하되, 교정 만삭시기의 검사는 26주 미만에서만 시행하도록 하고 있다[12]. 최근 개정된 대한신생아학회의 신생아진료 지침에서는 극소저체중출생아, 32주 미만의 조산아, 혹은 뇌출혈의 위험요소가 있다고 판단되는 신생아에 대하여 첫 검사를 생후 1주 이내에 시행하고, 출혈이 없는 경우에는 생후 1개월과 퇴원 시에 검사하고, 출혈이 있을 경우에는 합병증 발생을 확인하기 위해 더 자주 검사하도록 제시하고 있다[13].
일반적으로 미숙아에서 출생 1일에 시행하는 검사는 출생 전 손상과 선천기형을 확인하는 데 도움이 되지만, 만약 뇌손상을 의심할만한 소견이 없고 안정적인 상태의 신생아라면 최소 조작(minimal handling)을 위해 첫 검사를 4–7일까지 연기하기도 한다. 생후 첫 1주 이내에 시행하는 검사는 미숙아의 종자기질-뇌실내출혈 (germinal matrix-intraventricular hemorrhage, GMH-IVH), 뇌실주위출혈성경색(periventricular hemorrhagic infarction, PVHI), 소뇌출혈(cerebellar hemorrhage)의 발생을 확인할 수 있고, 생후 2–6주 사이의 검사는 PHVD, 뇌실주위백질연화증(periventricular leukomalacia, PVL), 감염에 의한 후유증 등을 확인할 수 있으며, 퇴원 시 혹은 교정 만삭시기의 검사는 뇌의 성숙과 이미 발생한 뇌손상의 영구적인 영향을 확인하기 위해 시행한다[3,14].
뇌부종과 관류장애는 비교적 초기에 확인되지만, 기저핵(basal ganglia)과 시상(thalamus)에 고에코 음영이 나타날 때까지는 2–3 일 정도가 걸리고, 대뇌 피질(cortical) 및 피질하(subcortical) 영역에서 뚜렷한 변화가 나타날 때까지는 5–7일 정도가 소요된다. 그러나 치료적 저체온요법을 적용하기 전에 선천성 뇌기형과 금기증인 중증뇌출혈 여부를 확인하기 위해 출생 1일에 검사를 시행할 수 있다[3].
초음파 기기에는 대부분 뇌 초음파에 적합한 설정이 미리 프로그램화되어 있으나 아기의 상태, 연령, 체중, 병태 등에 따라 개별적인 조작이 필요한 경우도 있다. 탐촉자(probe)는 컨벡스형(convex/curved)과 선형(linear) 탐촉자를 둘 다 사용하여 검사하는 것이 권장된다(Figure 1). 컨벡스형은 낮은 주파수로 깊은 부위의 구조물을 확인하기에 유용하고, 선형은 높은 주파수로 탐촉자에 가까운 구조물 확인하기에 적합하다[3]. 신생아의 경우에는 머리가 작아 심초음 파용의 섹터형(sector) 탐촉자로도 검사가 가능하다[15].
주파수는 일반적으로 7.5–11 MHz가 선호된다. 낮은 주파수는 투과성이 좋아 깊은 위치의 구조물을 잘 보여주지만, 상대적으로 해상도는 떨어진다. 확인하고자 하는 부위에 초점을 맞추면 해상도의 감소를 부분적으로나마 해소할 수 있다[3]. 깊이 조절은 정중시상면(midline sagittal plane)에서 후두골(occipital bone)을 다 확인할 수 있는 정도로 조절한다.
탐촉자를 음향창에 잘 고정하기 위해서는 엄지와 검지로 탐촉자를 잡은 뒤, 나머지 세 손가락으로 탐촉자를 아기 머리에 고정한다. 아기의 자세와 머리 위치에 무리가 없도록 주의한다. 탐촉자는 여러 아기에게 사용하기 때문에 감염 관리에 유의해야 하며, 겔은 따뜻하게 데워서 듬뿍 사용하도록 한다. 초극소저체중출생아(extremely low birth weight infant, ELBWI)에서는 탐촉자를 강하게 대는 것만으로도 두개내압이 항진되어 구토하거나, 혈압 등에 변화를 보일 수 있으므로 주의해야 하고, 가능하다면 수유 전에 검사하도록 한다.
신생아의 뇌를 초음파로 관찰할 수 있는 음향창으로는 대천문 (anterior fontanelle), 소천문(posterior fontanelle), 전측두 천문(sphenoid fontanelle 또는 temporal window), 후측두천문(mastoid fontanelle) 등이 주로 사용된다. 대천문은 천막상부(supratentorial)의 뇌 영상을 얻는 데 유용하지만, 천막하부(infratentorial)의 구조물을 확인하는 데에는 탐촉자와의 거리가 멀고 천막으로 인한 음영 증가가 있어 제한이 있다. 측정이나 기록을 하기 위해서는 고정 버튼(freeze)으로 영상을 고정시켜 저장해야 하며, 비디오레코딩(cinegraphic loop) 기능을 같이 이용하면 정지 영상에서 놓칠 수 있는 이상 소견을 확인하고 판독하는 데 도움이 될 수 있다[16,17].
표준 대천문 영상은 6개의 관상면(coronal planes) 영상과 5개의 시상면(sagittal planes) 영상을 포함한다[18].
탐촉자를 대천문의 가운데 두고 화면의 오른쪽에 뇌의 왼쪽이 위치하게 하여, 앞쪽의 전두엽(frontal lobes)부터 시작해서 뒤쪽의 후두엽(occipital lobes)으로 가면서 촬영한다(Figure 2). 좌우가 대칭이 되고, 반구사이열(interhemispheric fissure)이 화면의 가운데에 수직으로 위치하도록 노력한다.
전두엽의 앞부분을 충분히 살피기 위해 안와골(orbits)이 보이도록 충분히 기울여 영상을 얻는다. 일반적으로 뇌고랑(sulcus)은 고에코, 회백질은 저에코, 백질은 균질성의 고에코로 보이나, 회백질과 백질을 구별하기 힘들 수도 있다. 정중앙에는 반구사이열이 확인된다.
전각 측뇌실의 전각(frontal horns), 투명중격(cavum septum pellucidum), 뇌량(corpus callosum)을 포함한다. 측뇌실 전각의 크기는 양쪽이 비대칭적일 수 있다. 저에코의 투명중격이 양쪽 측뇌실의 전각 사이에서 확인될 수 있으며 아래로는 좌, 우 몬로공(foramen of Monro)이 내부의 맥락총(choroid plexus) 때문에 고에코로 나타난다. 측뇌실의 위쪽에는 뇌량이 두 줄의 트램라인(tramline) 모양으로 보이고, 양쪽 반구에서 실비우스열(Sylvian fissure)이 옆으로 누운 Y자 모양의 고에코로 나타난다.
제 3뇌실(third ventricle)과 측뇌실의 체부(body), 기저핵, 시상을 포함한다. 측뇌실의 체부가 가운데 상방에 존재하고, 내부에는 맥락총이 고에코로 보인다. 아래로 정중앙에 슬릿 모양(slit-like)의 제 3뇌실이 존재하며, 좌, 우 측뇌실의 체부와 제 3뇌실을 합치면 Y 자 모양으로 보인다. 제 3뇌실 옆으로는 난원형의 시상이 약간 고에코로 보이고, 시상 외측으로는 뇌와 비슷한 음영의 기저핵이 보이는데, 종종 선명하지 않을 수 있다. 기저핵과 시상에서 대칭적인 에코 증가가 있다면 부종이나 허혈, 출혈에 의한 소견일 수 있으므로 주의를 기울여야 한다. 미숙아라면 이 단면에서 GMH-IVH 발생 여부 를 확인하기 위해 미상시상구(caudo-thalamic groove)를 더욱 주의 깊게 살핀다.
전두엽과 측두엽(temporal lobes), 심부 회백질, 천막, 중뇌 (mesemcephalon), 소뇌충(cerebellar vermis)과 소뇌반구(cerebellar hemisphere)가 포함된다. 실비우스열의 상방에는 전두엽, 하방에는 측두엽이 보이고, 화면의 아래쪽에는 고에코의 소뇌천막과 그 사이로 뇌간(brain stem)과 소뇌의 일부가 확인된다. 뇌간은 뇌와 비슷한 에코를 보이고, 소뇌는 소뇌천막때문에 고에코로 보인다. 이로 인해 작은 소뇌출혈은 관상면에서 확인이 어려울 수 있다.
⑤ 다섯 번째: 측뇌실 체부-삼각부 양측 측뇌실의 내부에는 맥락총이 확인되고, 아래쪽으로 고에코의 소뇌가 확인된다. 뇌실주위백질은 균질한 고에코로 보이지만 맥락총보다 음영이 높지 않다. PVL이나 백질의 다른 병변이 확인될 수 있는 부위이므로 주의를 기울여야 한다.
뇌의 앞쪽이 화면의 왼쪽에 오게 하고, 정중시상면부터 탐촉자를 기울여가며 방시상면(parasagittal plane), 외측 방시상면(lateral parasagittal plane) 순서로 찍는다(Figure 3). 보통 중앙에서부터 오른쪽, 왼쪽 순서로 찍는다.
위쪽부터 대뇌반구 안쪽의 뇌고랑, 그 아래쪽 활모양의 뇌량, 그 아래로 새부리 모양의 제 3뇌실이 보인다. 제 3뇌실 천장에는 고에코의 맥락총이 확인되며, 뇌량과 제 3뇌실 사이에는 종종 투명 중격강이 확인된다. 삼각형의 저에코로 보이는 제 4뇌실의 앞쪽으로는 교뇌(pons), 뒤쪽으로 소뇌가 나타난다. 도플러 검사에서 전대뇌동맥(anterior cerebral artery, ACA)과 내대뇌정맥(internal cerebral vein, ICV)을 확인할 수 있는 단면이다.
거꾸로 된 C자 모양의 측뇌실의 삼각부(trigone), 후두각(occipital horn), 측두각(temporal horn)이 관찰된다. 맥락총은 측 뇌실의 안쪽을 따라 고에코로 보이는데, 삼각부에서 가장 굵게 보인다. 종종 IVH와 혼동될 수 있으나, 정상 맥락총은 출혈과 달리 후두각이나 전각까지 넘어가지는 않으며, 시간 경과에 따른 에코의 변화가 없고, 컬러 도플러에서 혈관 흐름이 나타난다는 점에서 구분된다[19]. 고에코의 난원형 시상은 측뇌실에 둘러싸여 있고, 앞쪽에 위치한 미상핵(caudate nucleus)과 시상과의 경계인 미상시상구는 GMH-IVH 발생이 확인되는 부위이므로 중요하다. 미상시상구를 잘 보려면 탐촉자의 머리는 가운데 쪽으로, 꼬리는 바깥쪽으로 살짝 돌리면서 기울이는 것이 도움이 된다.
일반적으로 음향창이 작기 때문에 얻을 수 있는 단면이 한정적이지만, 측뇌실의 삼각부와 후두각, 후두엽, 후두와(posterior fossa)의 구조물들을 관찰하기에 유용하다. 아기를 바로 눕힌 상태에서 머리를 한쪽으로 돌린 다음 접근한다.
외이도의 전상방 1 cm 정도에 탐촉자를 수평으로, 마커를 아기의 코 쪽으로 가게 하여 뇌간 주위의 수평면(transverse plane) 영상을 얻을 수 있다. 도플러 초음파로는 대뇌동맥고리(circle of Willis)를 확인할 수 있다.
탐촉자를 양쪽 귓바퀴(helix) 뒤쪽으로 1 cm, 귀이주(tragus)의 1 cm 상방에 두고 관상면과 수평면에서 소뇌와 뇌간 등을 관찰하기 위해 사용되며, 작은 소뇌출혈과 중대뇌동맥(middle cerebral artery)의 도플러를 확인하기에 유용하다[3].
도플러 초음파는 혈류속도 및 스펙트럼 파형을 측정할 수 있어 뇌 혈역학을 연구하는 데 유용하며, 신생아의 뇌병변이 대부분 혈관 기원이므로 모든 검사 시에 시행하는 것이 권장된다[18]. 대개 큰 동맥과 정맥들은 컬러 도플러 초음파에서 항상 나타나지만, 내경이 작거나 혈류속도가 느려 일시적으로만 보이거나 안 보이는 혈관들도 있다.
동맥에서 주로 측정에 사용되는 것은 ACA인데, 대천문을 통한 정중시상면에서 뇌량의 바로 앞을 지나고, 안정적으로 혈류를 측정할 수 있어 임상에서 가장 많이 사용된다. 초음파 입사각이 혈류와 평행하게 만나는 점에서 맥박파형(pulsed wave)을 확인하여 최고수축기 혈류속도(peak systolic velocity, PSV)는 파형의 최고점, 확장말기 혈류속도(end diastolic velocity, EDV)는 파형의 최저점, 평균 혈류속도는 복수 파형의 적분치의 평균으로 측정한다. 저항지수(resistive index, RI)는 (PSV–EDV)/PSV로 구하며, 대부분 자동 으로 계산된다(Figure 4A). 동맥의 혈류속도는 재태주령, 수면이나 각성 상태, 적혈구용적율, 혈압, 순환혈류량, CO2 분압, 초음파 입사 각도 등에 영향을 받으므로 절대값보다는 반복적인 측정을 통해 변화를 추적하는 것이 중요하다[20]. RI는 입사각에는 영향을 받지 않지만 혈류속도, 대뇌혈류량, 말초혈액 저항과 대뇌 자동조절능 등의 영향을 받는다. 정상 신생아의 RI는 0.65–0.9이고, 일반적으로 미숙아에게서 더 높고, 재태주령이 증가함에 따라 감소한다[21-23]. 수치가 클수록 혈관 저항이 크다는 것을 의미하며, 급성 저산소증이나 허혈이 있으면 뇌혈관의 확장이 생겨 확장말기 혈류가 늘어나므로 RI는 감소하고, 두개내압항진이나 동맥관개존증(patent ductus arteriosus, PDA) 등에서는 확장기 혈류가 감소하므로 RI가 상승한다[24]. 그러나 EDV가 높더라도 PSV가 현저히 낮으면 RI는 정상범위에 있을 수 있으므로, RI만으로 뇌혈류상태를 평가하는 것은 오류의 위험이 있다. 또한, 검사 시 탐촉자를 강하게 대는 것만으로도 두개내압이 항진되어 RI가 상승할 수 있으므로 해석에 주의가 필요하다[20].
정맥파는 일반적으로 연속파형(산과 골짜기가 없는 편평한 파형)이며, 측정치는 통상적으로 사용되지 않는다[17]. 대뇌정맥은 대부분 동맥과 동반되지 않으며, 판막이 없고 근육층이 발달되어 있지 않기 때문에 혈류의 흐름은 순전히 압력 차이에 의해 이루어진다. 동맥에 비해 변이가 많으며, 경로도 일정하지 않다. GMH-IVH의 발생 부위인 종자기질 부근의 심부정맥들은 좌, 우의 ICV에 예각으로 유입 되어 U자형을 만들면서 큰대뇌정맥(great vein of galen)으로 흘러 들어가며, 직정맥동(straight sinus)을 거쳐 심장으로 들어간다. ICV는 항상 보이는 혈관이므로 정중시상면에서 측뇌실의 아래쪽으로 주행하는 것을 쉽게 확인할 수 있다(Figure 4B). 단, 혈류속도가 느리기 때문에 스케일과 필터를 조절해야 한다. 근위부의 큰 정맥들은 때때로 울음, 자세, 호흡, 대천문의 압박 그리고 근접한 동맥의 맥박주기에 따라 맥박파형의 흔들림(fluctuation)을 보일 때도 있는 데에 반해, ICV는 속도가 느리고 그러한 영향을 덜 받기 때문에 ICV에서 나타나는 맥박파형의 흔들림(Figure 4C)은 흉곽내압의 변화, 심방압 상승, 정맥 울혈, 또는 자율조절능 손상 등의 가능성을 시사 한다[25]. 최근 고주파수 탐촉자의 사용과 초음파 기기의 발달로 작은 정맥들과 낮은 혈류속도도 평가가 가능해짐에 따라, 추후 대뇌정맥계에 대한 연구는 더욱 활발히 이루어질 것이 기대된다[26].
GMH-IVH의 분류에는 일찍이 Papile 등[27]이 제안한 분류가 아직도 통용된다(Table 1). Grade Ⅰ은 출혈이 뇌실막밑(subependymal) 종자기질에만 국한되어 있는 상태로 측뇌실의 미상시 상구에서 고에코 음영으로 나타난다(Figure 5). 일반적으로 수 일에서 수 주에 걸쳐 사라지거나, 3–5 mm의 낭포를 형성할 수 있다. Grade Ⅱ는 출혈이 측뇌실 안으로 퍼졌으나, 뇌실확장은 동반하지 않은 상태로 맥락총이나 후두각으로 튀어나온 혈전이 고에코로 나타난다. 뇌실확장을 동반하지 않기 때문에, 실제로는 진단이 어려운 경우도 많다. Grade Ⅲ는 편측 혹은 양측의 뇌실확장을 동반하므로 진단하기 쉽다. 출혈이 측뇌실을 채우고 있으며, 뇌실벽에 화학성 뇌실염을 일으키면 뇌실벽 에코가 상승하는 경우도 있다. Grade Ⅳ 는 편측 혹은 양측의 뇌실내출혈과 그와 인접한 뇌실주위 뇌실질에 고에코 영역이 확인되는 것을 통해 진단된다. 대부분이 전두엽과 두정엽(paritetal lobes)에서 발생하고, 편측성인 경우가 많다.
출혈 후 1–3주 후에 뇌실확장이 나타날 수 있으며, Grade Ⅲ 이상의 GMH-IVH는 출혈 시부터 이미 뇌실확장이 보일 수도 있다[11]. 측뇌실의 전각보다는 삼각부나 후두각의 확대가 선행되며, 중증 출혈일수록 뇌실 전체가 확대되기 쉽다. 뇌실 크기 측정에는 ventricular index (VI), ventricle/brain (V/B) ratio, anterior horn width (AHW), thalamo-occipital distance (TOD) 등이 주로 사용된다(Figure 6). VI는 몬로공이 보이는 관상면(제 3뇌실 단 면)에서 측뇌실의 외측 가장자리(lateral border)와 정중앙의 대뇌 낫(falx cerebri) 사이의 거리를 측정한 값이고, V/B ratio는 (VI-left+ VI-right)/biparietal diameter로 구하며, AHW는 측뇌실 전각의 가장 넓은 대각선 거리이다. TOD는 방시상면에서 시상의 가장 바깥쪽에서 측뇌실 후각의 가장 바깥쪽까지의 사이의 거리로 측정한다[28]. 일반적으로 VI >재태주령에 따른 참고치의 97th%, V/B ratio >0.35, AHW >3–6 mm, 또는 TOD >24.7 mm이면 PHVD 로 정의한다[28].
진행성 PHVD 환자에서 RI의 상승은 두개내압항진 가능성을 시사하며, 대천문을 탐촉자로 압박하여 측정하는 ΔRI (percentage of change in RI=post-compression RI–baseline RI/baseline RI, normal value: 1%–19%)는 PHVD의 중증도 판정과 치료 결정에 있어서 RI보다 예민하고 유용한 지표로 알려져 있다[29]. 그러나 대천문의 압박은 반복적으로 시도할 수 없고 정교한 테크닉이 필요하므로 숙련된 검사자에 의해 시행되는 것이 바람직하고, 검사자들 간의 측정값 차이가 있을 수 있으므로 해석에 주의가 필요하다[12,20].
GMH-IVH는 정맥의 출혈임이 이미 밝혀져 있으나[30,31], 발생기 전에는 다양한 인자들이 복잡하게 관여한다. 종자기질주위 미세혈 관구조의 취약성과 대뇌혈류의 변동성, 자동조절능의 부족 등의 요인에 정맥압의 변동, 정맥 해부구조의 변이, 유전적 요인 등이 더해져 작은 세정맥의 파열로 발생한다. 따라서 종자기질 주변 혈관들의 혈류 흐름과 변화를 살피는 것은 GMH-IVH의 위험을 예측하고 예방하는 데에 중요하다.
대뇌동맥의 혈류속도가 낮으면 재관류(reperfusion)시기에 GMH-IVH의 발생 위험이 있으며, 낮은 관류로 인해 허혈성 손상이 유발될 위험도 있다. 반대로 높은 대뇌동맥 혈류속도는 평균동맥압 상승과 연관되므로 혈관의 직접적인 파열 위험성이 있다[20]. 자동조절능의 부족은 평균 동맥압의 변동에 따라 혈류속도가 급격히 따라 변화하는 것으로 확인할 수 있으며[20], 이는 GMH-IVH의 발생 위험을 높이는 것으로 알려져 있다[32]. ELBWI에서 대뇌동맥의 확장말기 혈류의 소실은 GMH-IVH 발생의 의미있는 예측인자로 보고된 바 있고, PDA와도 관련이 있었다[33].
대뇌정맥의 혈역학적 소견과 GMH-IVH 발생 위험에 대해서는 아직 충분한 연구가 이루어지지는 않았으나, Ikeda 등[34]은 도플러 초음파에서 ICV의 맥박파형에서 흔들림이 심한 경우에 IVH 발생과 관련됨을 보고하였다. 연구자들은 ICV 맥박파형의 흔들림을 4단계로 분류하였는데, Grade 0은 정상 파형으로 혈류속도가 일정한 것; Grade 1은 흔들리는 파형이지만 혈류속도의 최저치가 최대치의 절반 이하로 떨어지지 않는 것; Grade 2는 흔들리는 파형이며 혈류속도의 최저치가 최대치의 절반 미만인 것; Grade 3은 흔들리는 파형이며 부분적으로 중단되어 혈류속도의 일부가 0 m/s가 되는것으로 나누었다. 총 80명의 ELBWI에서 초기 144시간 동안 ICV 맥박파형을 정기적으로 평가하였을 때, Grade 2 이상의 심한 흔들림이 있는 환자군에서 IVH의 발생이 많았다[34]. 그러나 ICV와 달리 큰대뇌 정맥이나 직정맥동 같은 근위부의 큰 정맥에서는 맥박파형의 박동 성 흔들림이 비교적 흔하게 관찰되었고, IVH 발생과 관련이 없었다[35]. Tanaka 등[36]도 두 명의 미숙아 증례에서 ICV의 맥박파형이 부분적으로 역전되거나 끊김이 확인되었을 때 IVH가 발생한 것을 확인하였고, IVH 발생 후에는 ICV 맥박파형의 흔들림이 해소되었다고 보고하였다. ICV 맥박파형의 역전이나 중단은 우심방의 압력 증가가 두개 내로 전달되어 발생하는 것으로 보이며[36], 만삭아에서는 중심정맥압이 증가하여도 ICV의 흔들림이 발견되지 않는 점을 고려하면, 미숙아에서의 ICV가 중심정맥압의 증가에 더 취약할 가능성이 있다[25,37,38].
따라서 미숙아의 뇌 초음파에서 이러한 대뇌혈류의 변동이 확인되면, 신속하게 심초음파 검사를 시행하고, 진정치료, 혈역학적 이상의 교정, 후부하 감소를 위한 조치, 기계환기기 조절 등의 중재적 노력을 고려해야 한다. Ikeda 등[39]은 앞서 제시한 연구에서 ELBWI에서 ICV 파형 흔들림이 확인되면, 혈압이 상승되어 있는 경우에는 혈압 강하제를 투여하고, PDA의 증후화가 있는 경우에는 PDA를 치료함으로써 ICV의 흔들림이 개선되었다고 보고하였다. ICV 파형 흔들림에 대한 치료 전략에 대해서는 더욱 체계적인 추가 연구가 필요할 것이다. 그러나 아직 뚜렷한 인과관계가 밝혀진 것은 아니라 할지라도, ELBWI의 급성기 순환관리에서 ICV에 대한 평가는 GMH-IVH의 예방으로 이어질 가능성이 있지 않을까 기대해 본다.
뇌 초음파는 안전성과 편리성에도 불구하고, 검사 시행 및 결과 해석에 있어서 검사자의 주관적인 요소가 상대적으로 크다. 따라서 정확하고 일관된 검사를 위해 오랜 숙련이 필요하다. 또한 자기공명 영상에 비해 작은 뇌실질출혈이나 허혈성 병변, 경도의 미만성 백질 손상의 확인에는 제한이 있다는 점을 염두에 두어야 한다. 전 세계적으로 현장 초음파의 활용이 증가함에도 불구하고, 체계화된 교육을 받을 기회의 부족, 오진이나 법적 문제에 대한 두려움, 영상의학과와의 영역 갈등, 처방과 보험 청구 문제, 초음파 기기의 가용성 등은 신생아 의사의 적극적인 검사 시행에 장애물이 되고 있다[6,40]. 그러나 신생아 의사에 의한 검사가 영상전문의에 의한 진단적 검사를 대체할 수는 없다는 한계를 인식하고, 정확한 진단을 내리는 것을 목표로 하기보다는 이상 소견이 의심되면 신속한 의뢰를 통해 조기에 진단적 검사가 이루어지도록 해야 할 것이다.
NICU에서 뇌 초음파는 중증의 미숙아와 고위험 신생아의 빠른 진단과 치료 및 예후 예측을 위해 필수적이다. 특히 도플러 초음파를 이용한 뇌혈류평가는 미숙아에서 뇌 보호를 위한 순환 관리에 중요한 정보를 제공한다. 신생아 의사로서 뇌 초음파를 직접 시행하기 위해서는 중요한 해부학적 구조들의 정상 소견을 이해하고, 적절한 테크닉으로 표준화된 영상을 얻을 수 있도록 표준지침서나 가이드라인을 최대한 활용하여 반복적으로 검사하고 판독해 보면서 친숙해지려는 노력이 필요하다. 그러나 비록 영상전문의 수준의 영상 확보는 아니더라도, 실시간 임상 상황에서 꼭 필요한 해부학적 혹은 혈역학적 정보를 얻는 데에 집중하여 신속하게 검사를 시행함으로써 아기의 변화를 조기에 파악하고 치료계획을 세운다면, 뇌손상을 예방하고 환자의 예후를 향상시키는 데에 도움이 될 것이다. 이를 위해서는 국내에서도 신생아 의사들이 다양한 현장 초음파를 보다 쉽게 배우고 훈련할 수 있는 체계적인 교육프로그램의 도입이 필요하다.
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Figure 1.
Three different types of probes. (A) Convex (curved) probe. (B) Linear probe. (C) Sector (phased array) probe.
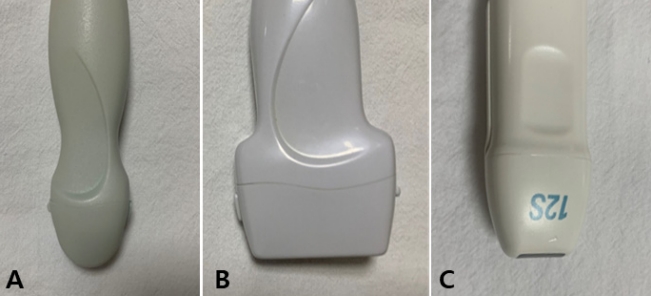
Figure 2.
Standard coronal images of the brain through the anterior fontanelle. (A) First standard coronal image through the frontal lobes. (B) Second coronal image through the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles. (C) Third coronal image through the third ventricle. (D) Fourth coronal image at the level of the cerebellum. (E) Fifth coronal image through the trigone of the lateral ventricle. (F) Sixth coronal image through the occipital lobes.
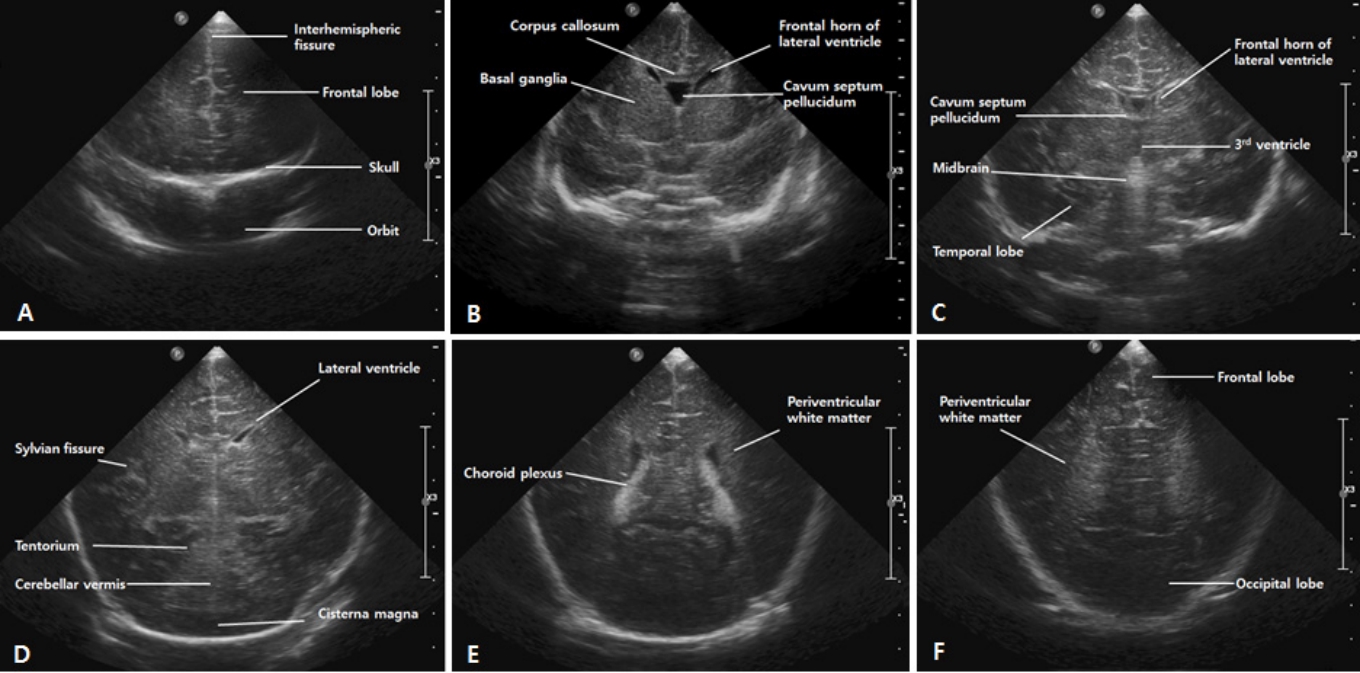
Figure 3.
Standard sagittal images of the brain through the anterior fontanelle. (A) Midline sagittal image. (B) Parasagittal image. (C) Lateral parasagittal image.
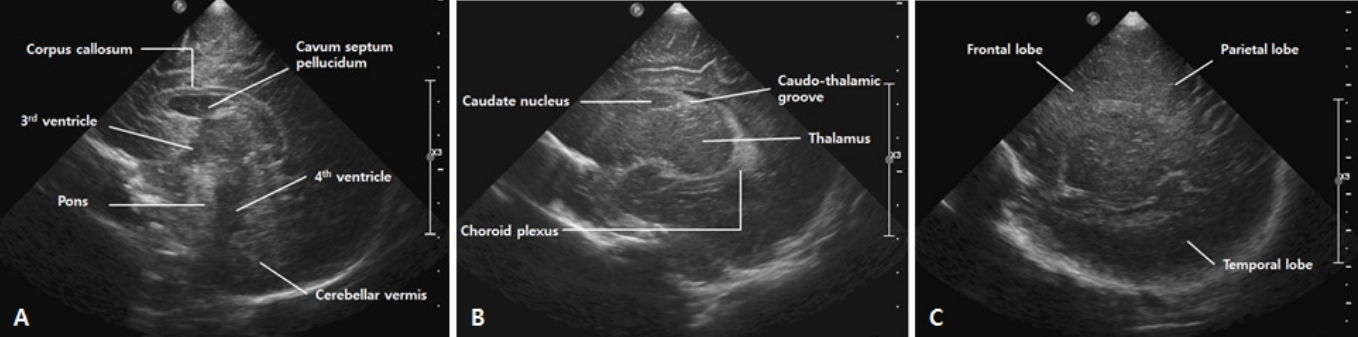
Figure 4.
Color and pulsed Doppler evaluation in the midline sagittal plane. (A) Resistive index (RI), peak systolic velocity (PSV) and end diastolic velocity (EDV) in the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) are automatically evaluated using spectral Doppler tracings. (B) Perfusion waveform of the internal cerebral vein (ICV) shows a steady waveform with a constant perfusion speed (Grade 0 fluctuation). (C) Perfusion waveform of the ICV fluctuates; however, the minimum speed is never less than half the maximum speed (Grade 1 fluctuation).
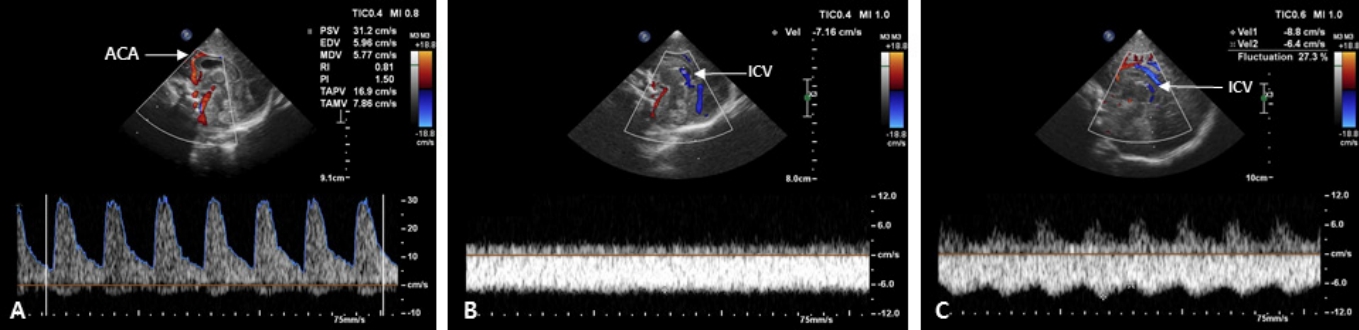
Figure 5.
Ultrasound findings of germinal matrix-intraventricular hemorrhage (GMH-IVH). (A,B) Grade I GMH-IVH. The location of the echogenic clot (arrows) at the right caudothalamic notch is typical of grade I GMH-IVH. (C,D) Grade II GMH-IVH. Coronal scan shows echogenic clot involving the caudate nucleus (arrows). Parasagittal scan shows the same clot centered at the caudothalamic notch (arrows) and the intraventricular hemorrhage within the occipital horn separate to choroid plexus (arrowhead). (E,F) Grade III GMH-IVH. Coronal scan shows a large left GMH-IVH (arrows) with intraventricular blood acutely distending its lateral ventricle. Note also the enlarged temporal ventricular horns. A small amount of blood in the right lateral ventricle (arrowhead) is present. Parasagittal view shows that the left grade III GMH-IVH fills >50% of the distended lateral ventricle. (G,H) Grade IV GMH-IVH. Coronal scan showing a left-sided grade III GMH-IVH (arrowhead) and large echodensity in the left frontoparietal white matter (arrow). Smaller right-sided grade II GMH-IVH (arrowhead). Left parasagittal scan showing the periventricular echodensity (arrows) extending from the posterior frontal white matter to the parietal white matter.

Figure 6.
Measurements of the ventricle size in post-hemorrhagic ventricular dilatation. (A) Measurements of the ventricular index (VI), anterior horn width (AHW), and ventricle/brain ratio on coronal scan. (B) Measurements of the thalamo-occipital distance (TOD) on sagittal scan.
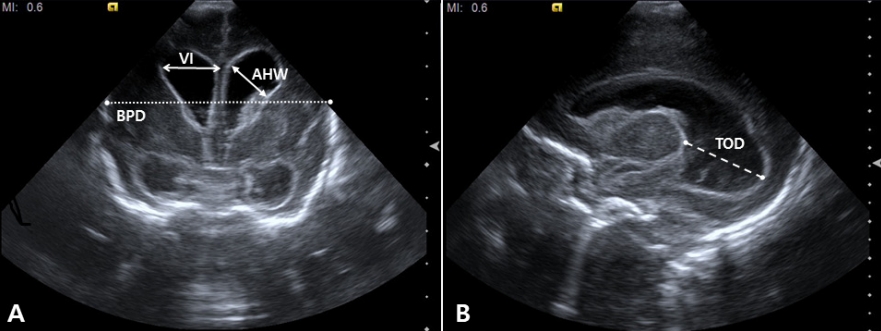
Figure 7.
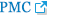
Ultrasound findings in a preterm infant (24 weeks of gestational age) with periventricular leukomalacia. (A) Coronal scan shows scattered hyperechoic lesions in the periventricular white matter. (B) Coronal scan 4 weeks later shows multiple cysts extending from the frontal lobe to the trigone area.
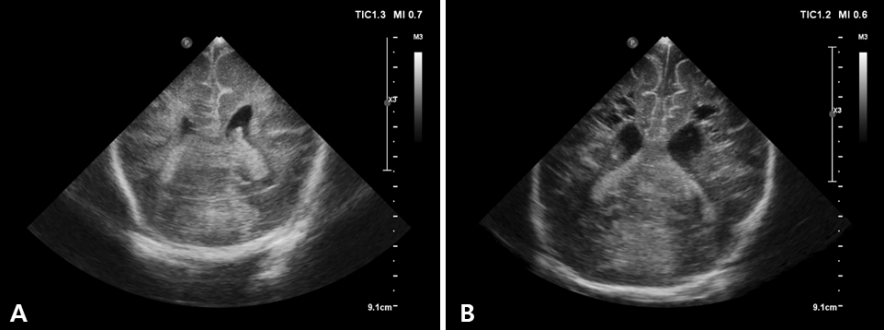
Figure 8.
Ultrasound findings in a preterm infant (25 weeks of gestational age) with bilateral intraventricular hemorrhage and left periventricular hemorrhagic infarction (PVHI). (A) Coronal scan shows a large echodensity in the left frontoparietal white matter. (B) Coronal scan 2 weeks later shows cystic degeneration following the PVHI with echogenic clot debris.
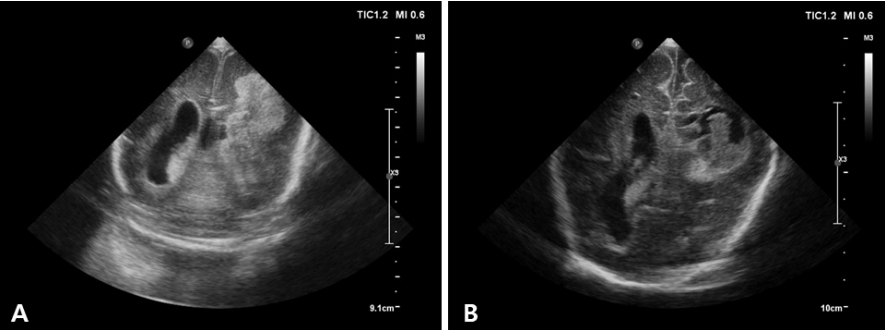
Table 1.
Grading System for the Germinal Matrix-Intraventricular-Hemorrhage by Papile [27]
REFERENCES
1. Kurepa D, Boyar V, Zaghloul N, Beachy J, Zaytseva A, Teng D, et al. Sructured neonatal point-of-care ultrasound training program. Am J Perinatol 2021;38:e284–91.


2. Ben Fadel N, Pulgar L, Khurshid F. Point of care ultrasound (POCUS) in Canadian neonatal intensive care units (NICUs): where are we? J Ultrasound 2019;22:201–6.


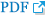
3. Dudink J, Jeanne Steggerda S, Horsch S, eurUS.brain group. State-of-the-art neonatal cerebral ultrasound: technique and reporting. Pediatr Res 2020;87(Suppl 1): 3–12.



4. Riedesel EL. Neonatal cranial ultrasound: avanced techniques and image interpretation. J Pediatr Neurol 2018;16:106–24.

5. Evans N, Gournay V, Cabanas F, Kluckow M, Leone T, Groves A, et al. Point-of-care ultrasound in the neonatal intensive care unit: international perspectives. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2011;16:61–8.


6. Singh Y, Tissot C, Fraga MV, Yousef N, Cortes RG, Lopez J, et al. International evidence-based guidelines on Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS) for critically ill neonates and children issued by the POCUS Working Group of the European Society of Paediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC). Crit Care 2020;24:65.



7. Miller LE, Stoller JZ, Fraga MV. Point-of-care ultrasound in the neonatal ICU. Curr Opin Pediatr 2020;32:216–27.


8. AIUM practice parameter for the performance of neurosonography in neonates and infants. J Ultrasound Med 2020;39:E57–61.


9. McLean G, Malhotra A, Lombardo P, Schneider M. Cranial ultrasound screening protocols for very preterm infants. Ultrasound Med Biol 2021;47:1645–56.


10. Hand IL, Shellhaas RA, Milla SS, Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Section on Neurology, Section on Radiology. Routine neuroimaging of the preterm brain. Pediatrics 2020;146:e2020029082.


11. Inder TE, de Vries LS, Ferriero DM, Grant PE, Ment LR, Miller SP, et al. Neuroimaging of the preterm brain: review and recommendations. J Pediatr 2021;237:276–87.


12. Mohammad K, Scott JN, Leijser LM, Zein H, Afifi J, Piedboeuf B, et al. Consensus approach for standardizing the screening and classification of preterm brain injury diagnosed with cranial ultrasound: a Canadian perspective. Front Pediatr 2021;9:618236.



13. The Korean Society of Neonatology. Manual of Neonatal Care. 4 ed. Seoul:The Korean Society of Neonatology, 2021, pp 376–84.
14. Beltempo M, Wintermark P, Lemyre B, Shalish W, Martel-Bucci A, Narvey M, et al. Predictors of severe neurologic injury on ultrasound scan of the head and risk factor-based screening for infants born preterm. J Pediatr 2019;214:27–33.


15. Ecury-Goossen GM, Camfferman FA, Leijser LM, Govaert P, Dudink J. State of the art cranial ultrasound imaging in neonates. J Vis Exp 2015;96:e52238.



16. O'Dell MC, Cassady C, Logsdon G, Varich L. Cinegraphic versus combined static and cinegraphic imaging for initial cranial ultrasound screening in premature infants. Pediatr Radiol 2015;45:1706–11.


17. James AC. Practical guide to neonatal cranial ultrasound (crus): basics. Paediatr Child Health 2018;28:424–30.

18. Caro-Dominguez P, Lecacheux C, Hernandez-Herrera C, Llorens-Salvador R. Cranial ultrasound for beginners. Transl Pediatr 2021;10:1117–37.



19. Maller VV, Cohen HL. Neurosonography: assessing the premature infant. Pediatr Radiol 2017;47:1031–45.


20. Couture A, Veyrac C, Baud C, Saguintaah M, Ferran JL. Advanced cranial ultrasound: transfontanellar Doppler imaging in neonates. Eur Radiol 2001;11:2399–410.


21. Horgan JG, Rumack CM, Hay T, Manco-Johnson ML, Merenstein GB, Esola C. Absolute intracranial blood-flow velocities evaluated by duplex Doppler sonography in asymptomatic preterm and term neonates. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1989;152:1059–64.


22. Romagnoli C, Giannantonio C, De Carolis MP, Gallini F, Zecca E, Papacci P. Neonatal color Doppler US study: normal values of cerebral blood flow velocities in preterm infants in the first month of life. Ultrasound Med Biol 2006;32:321–31.


23. Ecury-Goossen GM, Raets MM, Camfferman FA, Vos RH, van Rosmalen J, Reiss IK, et al. Resistive indices of cerebral arteries in very preterm infants: values throughout stay in the neonatal intensive care unit and impact of patent ductus arteriosus. Pediatr Radiol 2016;46:1291–300.



24. Lowe LH, Bailey Z. State-of-the-art cranial sonography: part 1, modern techniques and image interpretation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011;196:1028–33.


25. Taylor GA. Intracranial venous system in the newborn: evaluation of normal anatomy and flow characteristics with color Doppler US. Radiology 1992;183:449–52.


26. Camfferman FA, de Goederen R, Govaert P, Dudink J, van Bel F, Pellicer A, et al. Diagnostic and predictive value of Doppler ultrasound for evaluation of the brain circulation in preterm infants: a systematic review. Pediatr Res 2020;87(Suppl 1): 50–8.



27. Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr 1978;92:529–34.


28. Dorner RA, Burton VJ, Allen MC, Robinson S, Soares BP. Preterm neuroimaging and neurodevelopmental outcome: a focus on intraventricular hemorrhage, post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus, and associated brain injury. J Perinatol 2018;38:1431–43.



29. Taylor GA, Madsen JR. Neonatal hydrocephalus: hemodynamic response to fontanelle compression: correlation with intracranial pressure and need for shunt placement. Radiology 1996;201:685–9.


30. Nakamura Y, Okudera T, Hashimoto T. Microvasculature in germinal matrix layer: its relationship to germinal matrix hemorrhage. Mod Pathol 1991;4:475–80.

31. Ghazi-Birry HS, Brown WR, Moody DM, Challa VR, Block SM, Reboussin DM. Human germinal matrix: venous origin of hemorrhage and vascular characteristics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1997;18:219–29.


32. Van Bel F, Van de Bor M, Stijnen T, Baan J, Ruys JH. Aetiological rôle of cerebral blood-flow alterations in development and extension of peri-intraventricular haemorrhage. Dev Med Child Neurol 1987;29:601–14.


33. Julkunen M, Parviainen T, Janas M, Tammela O. End-diastolic block in cerebral circulation may predict intraventricular hemorrhage in hypotensive extremely-low-birth-weight infants. Ultrasound Med Biol 2008;34:538–45.


34. Ikeda T, Amizuka T, Ito Y, Mikami R, Matsuo K, Kawamura N, et al. Changes in the perfusion waveform of the internal cerebral vein and intraventricular hemorrhage in the acute management of extremely low-birth-weight infants. Eur J Pediatr 2015;174:331–8.


35. Ikeda T, Ito Y, Mikami R, Matsuo K, Kawamura N, Yamoto A, et al. Fluctuations in internal cerebral vein and central side veins of preterm infants. Pediatr Int 2021;63:1319–26.


36. Tanaka K, Sakamoto R, Imamura H, Naramura T, Matsumoto S, Iwai M, et al. Reversal of blood flow in deep cerebral vein in preterm intraventricular hemorrhage: two case reports. BMC Pediatr 2020;20:517.



37. Dean LM, Taylor GA. The intracranial venous system in infants: normal and abnormal findings on duplex and color Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1995;164:151–6.


38. Pooh RK, Pooh KH, Nakagawa Y, Maeda K, Fukui R, Aono T. Transvaginal Doppler assessment of fetal intracranial venous flow. Obstet Gynecol 1999;93(5 Pt 1): 697–701.


-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 4,068 View
- 123 Download
- Related articles in NM
-
Quality Improvement in Neonatal Intensive Care Units2018 May;25(2)
Prevention of Fungal Infection in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit.2013 August;20(3)
Deaths in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit between 2002 and 2014.2016 February;23(1)